Another magical trip to the North Sea and Never Never Land. This time starting with Amrum and then to Helgoland again. Depite whistful (sic) and fun memories, the trip ended on a sad note as my dear friend’s mother died while we were returning to harbour. So perhaps just some photos:
Friendships Better Than Professorships?
 This month we, the Trustees of Gresham College, hosted the Lord Mayor’s Gresham Event at Guildhall (he or she is our President!) … http://www.gresham.ac.uk/london-the-global-maritime-centre-in-a-changing-world
This month we, the Trustees of Gresham College, hosted the Lord Mayor’s Gresham Event at Guildhall (he or she is our President!) … http://www.gresham.ac.uk/london-the-global-maritime-centre-in-a-changing-world
London – The Global Maritime Centre in a Changing World
ChainZy – Anchoring Mutual Distributed Ledgers (aka blockchains) In Reality
Over the Last year there was a lot of hype about mutual distributed ledgers (MDLs, aka blockchain technology). Leaving aside the coin-based systems of Bitcoin, Ripple, and Ethereum, I think Z/Yen’s practical work in the field is fascinating. Much of Z/Yen’s work was featured in the FT recently.
We have been working with mutual distributed ledger (MDL) technologies since 1995 for complex multi-party transactions, but until recently financial services people dismissed MDLs as too complex and insecure, until Bitcoin terrified them. The mania around cryptocurrencies has led to a reappraisal of their potential. Equally, MDLs are getting easier to implement and manage at a time when people are rethinking the future of financial services.
Z/Yen have a lot of work on, a project with SWIFT on The Impact and Potential of Blockchain on the Securities Transaction Lifecycle, ‘proof of concept’ and ‘use case’ demonstrators for clients, courses, and ongoing research. Z/Yen and Long Finance share their research widely, e.g.:
| Sharing Ledgers For Sharing Economies: An Exploration Of Mutual Distributed Ledgers (aka blockchain technology) | Michael Mainelli and Mike Smith | 2015 |
Journal of Financial Perspectives, Volume 3, Number 3, EY Global Financial Services Institute (December 2015), 44 pages.
|
Z/Yen published the work of one significant 2015 research consortium (InterChainZ) online back in September. InterChainZ has been working for the past year on multiple MDLs working together. Z/Yen used their suite of MDL technologies built up over two decades, dubbed ChainZy, to build a set of seven ‘use cases’ working together. InterChainZ aimed to answer a core question – “what elements of a trusted third party are displaced by mutual distributed ledger (MDL) technology?” by providing a basic demonstrator of MDLs, including variants of blockchains, and comparing how they might work within selected financial services use cases. InterChainZ provides a generic demonstration suite  of software providing an interface to MDLs for tasks such as:
of software providing an interface to MDLs for tasks such as:
- selection & storage of documents;
- document encryption;
- sharing keys;
- viewing the MDL transactions;
- viewing the MDL contents subject to encryption structures.
The software permitted the testing of a variety of MDL technical configurations. It was then employed to discuss and test various practical applications of MDLs. The outputs were shared with participants as joint intellectual property for their own future use.
InterChainZ has shared some learning online. This includes the above video – titled “Boring is Brilliant” – where participants (DueDil, PwC, and SunCorp) explain what mutual distributed ledgers are, and how they could be employed. A few of the key learning points from InterChainZ were:
Terminology: Early in the InterChainZ project it became apparent that the further discussion moved away from Bitcoins and blockchains, the easier conversations became. Bitcoins and blockchains were burdened with too much baggage. Terminology is evolving rapidly, hence the team’s emphasis on “mutual distributed ledgers” as the term of choice. The technical focus might be on boring ‘ledgers’, but the excitement is in the applications above.
Identity: It also became clear that ‘identity’ issues are universal. One of the great advantages of doing consortium research was that the identity chains were both ‘use cases’ and essential infrastructure that would have had to be built for anything else of substance. Distinguishing ‘identity’ from ‘transactions’ and ‘content’ made processing and distribution sense, at the expense of a bit more complexity in comprehension. While InterChainZ showed that MDLs can work together, and the project explored many different architecture possibilities, what was explored is certainly only a small portion of what is possible.
Architecture Choices: MDL architecture has to reflect the economic and commercial realities of numerous businesses working together. This dictates that many different architectures are needed for many different situations. One ‘blockchain’ will not suffice for most business-to-business work. Different business uses require different node structures. For example, the Master node architecture would be appropriate where a regulator is confirming all transactions in a market as being from valid market participants. The Supervisor node architecture might suit a small group of large organisations interacting with multiple smaller ones.
Validation: Core to identity and architecture is the method used for validating new transactions. While Bitcoin blockchain’s ‘proof-of-work’ validation approach is fascinating, and suited to having seven billion people confirm retail transactions, it is not appropriate for wholesale markets. One of the basic premises for InterChainZ was to focus on exploring “non-blockchain consensus or identity” MDLs, i.e. what benefits could be achieved when not using currencies or tokens. This decision provoked some external criticism, principally questioning whether there were benefits to MDLs without proof-of-work validation mechanisms. However, Z/Yen long ago achieved around 1 billion transactions per day, a benchmark a few are now touting, by sacrificing token systems for other validation methods.
Content Chains: The project developed a number of MDLs that directly stored documents, as well as MDLs that only recorded the ‘hash’ of documents. This led to the development three conceptual MDLs, “identity chains”, “transaction chains”, and “content chains”. Corporate and individual identity chains authorise access to a transaction chain. A transaction chain holds the core ledger records of all transactions, but only a hash of original documents. The content chain is an MDL holding all of the original documents. The content chain might be managed by a third party for storage and retrieval because of its size. This conceptual structure is quite flexible. The only technical difference between the chains is that the identity and content chains have a fixed length hash field while the content chain has a variable length field.
Further Research – IntereXchainZ & MetroGnomo
At a basic level, the project showed that MDLs work and can work together, but current research, IntereXchainZ goes much further, pushing forward four themes:
Simplify
- market functions – order matching, margining, account functions, clearing, settlement, as well as possible uses of a token currency within exchange;
- usability and ergonomics to enhance the end-user experience – exploring the end-user experience by connecting to off-the-shelf wallets for cryptographic key management;
Integrate
- integrity proofing – dynamic anomaly and pattern response additions, monitoring and testing facilities;
- Content Hash-Addressable Storage Market (C#ASM) – extending the ‘identity’, ‘transaction’, and ‘content’ chain thinking that emerged from InterChainZ into an indexable archiving system both as a ledger itself, but also supporting other ledgers;
- data taxonomies, encryption levels and tracking – how feasible is it to have differently labelled categories and ‘data boxes’ (e.g. health, car insurance, home insurance, driving record, etc. on a person’s MDL) that can only be opened as a group, to encrypt levels with levels (first order health data perhaps before detailed data), to provide access records (who opened, when), and might homomorphic encryption have a role;
Automate
- facilities for automated creation of new mutual distributed ledgers – a parameter driven system providing options for permission management, proof of stake and identity settings, supervisor-master and other node settings, ‘voting’ permutations, and peer-to-peer structure settings;
- exchange functions – processes to make the basic interacting ledgers into a demonstrator of a full exchange, with numerous ‘use cases’ therein, e.g. sharing identity functions with transactional functions and storing relevant documents securely and permanently;
Control
- management and control features – management information, performance statistics, visualisation;
- documentation of standards for mutual distributed ledgers and legal entity identifiers.
And 2016? Z/Yen are launching a new timestamping service next month with the support of at least one government. We call it MetroGnomo, a “world record service”. This is being launched in an experimental mode using MDLs based on ‘agnostic broadcasting’. The intention is to increase speeds further, increase resilience, and provide a useful, free service showcasing Z/Yen’s technologies.
Reprise Of The Morgensprache
During the week of the Lord Mayor’s Show it was our turn to host the Hamburger Morgensprache back in London. We were delighted to be able to host them at two events. The first event was a Freedom Ceremony on Friday, 13 November:
As ever, Murray Craig, Clerk of the Chamberlain’s Court, City of London, provided one of his delightfully witty, historical, and theatrical presentations, with a traditional round of Madeira to toast the “Youngest Freemen”. Perhaps the most touching thing the City of London did was to dig out from the archives this parchment from 1342!

A writ under King Edward II’s Privy Seal bidding the Mayor, Aldermen & Commonalty to allow the merchants of Almaine to enjoy their ancient franchise to sell wine and other merchandise was read in the Mayor’s Court on 13 November 1342.
The following morning of the show, 14 November, the Worshipful Company of World Traders hosted the team for a breakfast at the Capital Club, before everyone headed off to join their floats, have a wonderful Show, and get drenched!
Hamburger Morgensprache
“Handelskammer Hamburg” is the Chamber of Commerce for Hamburg – https://www.hk24.de/. Unlike British or American chambers, German Handelskammers have statutory powers and levy charges on businesses. Their compulsory status also encourages leading businesspeople to participate more earnestly in commerce and trade policy issues. Starting with an initiative by Lord Mayor Michael Savory and Kenneth Stern, and picked up by Aldermen Alison Gowman, and Jeffrey Evans, they provide a float in the Lord Mayors’ Show every other year. Equally, each year two Aldermen go to Hamburg representing the City at the Handelskammer’s big annual celebration in October, the Morgensprache. 2015 would have been an ‘away’ year for the Hamburgers, but in honour of Lord Mountevans’ Mayoralty they made a special trip this year to be in the show.
One of the most delightful trips we’ve made recently was when Elisabeth and I had a quasi-diplomatic mission to Hamburg, accompanying Alderman Alison Gowman and Murray Craig, Clerk of the Chamberlain’s Court, City of London, where we too became part of this initiative. The purpose of the mission was to deepen links with Hamburg for the benefit of both, a celebration of trade.
The Hanseatic links between London and various North Sea and Baltic ports are crucial in understanding history and where we are today, yet they get mistier. Few remember that the Hanseatic League maintained a Kontor (a medieval free trade zone) called the ‘Stalhof’ or ‘Steelyard‘ in the heart of London from 1266 till the merchants were thrown out in 1598 by Queen Elizabeth I. Though they returned, the Hanseatic League had certainly ceased trading by 1758. That said, Lübeck, Bremen and Hamburg only sold their common property, the London Steelyard, to the South Eastern Railway in 1852. Cannon Street station was built on the site and opened in 1866.
This link to the Hanse event and transcripts might interest – http://www.gresham.ac.uk/london-forgotten-hanseatic-city. My particular interest is here – http://www.gresham.ac.uk/sites/default/files/14jun07michaelmainelli_hanseanditsinfluence.doc
Our hosts were Handelskammer Hamburg (Hamburg Chamber of Commerce). Hamburg welcomed us most warmly. We learned a lot as well, particularly about the role of compulsory Chambers of Commerce and how that probably makes German apprenticeships far more successful than the British sort. They are full of pride about their City and their achievements, reminding me of a wonderful quote – “Bürgermeister Johann Heinrich Burchard (1852-1912) bemerkte zu der Nachricht, seine Majestät geruhe, Rudolph Schröder (1852–1938) in den Adelsstand zu erheben, Majestät könne ihn zwar in den Adelsstand ‘versetzen’, in ihn ‘erheben’ könne sie einen hanseatischen Kaufmann jedoch nicht.”
“Mayor Johann Heinrich Burchard (1852-1912) reacted to the news that it would please his Majesty to deign to raise Rudolph Schroeder (1852-1938) to the nobility by noting that his Majesty could indeed ‘place’ him in the peerage , however as a Hanseatic merchant he could never be ‘elevated’.”
[Renate Hauschild-Thiessen: “Adel und Bürgertum in Hamburg. In: Hamburgisches Geschlechterbuch”. 14, 1997, S. 21–32.]
Our visit was well-covered and it is difficult to think of a more generous group of hosts than the ones we had. We toasted each other merrily with their traditional “Cheese and Bread”, an ancient London shibboleth for the German-speaking community during the days of the Kontor in London at the Stalhof. THE HANSEATIC STEELYARD IN DOWGATE, by Alderman Alison Gowman in Mansion House on18 October 2013.
Perhaps not a speech full of content, but certainly full of warm feelings, I reproduce the text of my speech followed by an English translation:
Morgensprache – Deutsche
15 October 2015, Handelskammer Hamburg
Ältermann, sehr geehrte Damen und Herren, liebe Kolleginnen und Kollegen aus London,
Ich darf Sie herzlich von Alan Yarrow, The Rt Hon Lord Mayor of London, und seinen Sheriffs sowie dem Rat der Aldermen und Councilmen grüssen. Wir möchten von London nach Hamburg dem anhaltenden Erfolg Ihrer Morgensprache gratulieren.
Als Professor für Handel liebe ich eine Stadt, die den Handel feiert. Unsere beiden Städte sind sehr unabhängig. Die Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg ist ein stolzer Stadtstaat seit dem 9. Jahrhundert. Die City of London ist die älteste kontinuierliche Demokratie in der Welt. Unsere beiden Städte sind im Handel über die Jahrhunderte verbunden. Am 8. November 1266 wurde ein Vertrag zwischen Hamburger Kaufleuten und Henry III von England geschlossen um eine Hanse in London zu etablieren – das erste Mal in der Geschichte wurde dieser Begriff für die Liga eingesetzt.
Unsere deutschen Verbindungen sind stark. Meine Frau kommt aus Franken. Meine Großmutter war Deutsche. Aber ich habe nie eine formelle Rede in Deutsch gegeben, so dass ich fast, wie in Franken, mit ‘Grüß Gott’ begann. Wir besuchen oft Freunde in Ihrer altehrwürdigen und lebendigen Stadt. Ich nahm jedes Jahr während den 2000er Jahren an der Kieler Woche teil. Meine Frau und ich sind in der Schifffahrt mit einem kommerziellen, und auch altehrwürdigen, Segelboot tätig und gehören der Gilde der Worshipful Company of Watermen & Lightermen an. Aber wir haben nie mit dieser Ehre gerechnet, heute zu Ihnen sprechen zu dürfen. Vielen Dank.
Unsere beiden Städte haben viel gemein – Schifffahrt, Technologie, Finanzen, Kunst, Medien und Verlagswesen – aber das Wichtigste, was unsere Städte vereint, ist die ähnliche Denkweise.
Eines Tages fragte eine Lehrerin, Frau Müller, ihren Schüler Johnny, „Johnny, wenn zwei Vögel auf einer Leitung sitzen, und ich feuere zwei Schüsse aus einer Schrotflinte, wie viele Vögel werde ich treffen?“ „Einen, Frau Müller.“ „Johnny, hör mir genau zu, wenn zwei Vögel auf einer Leitung sitzen, und ich feuere zwei Schüsse aus einer Schrotflinte, wie viele Vögel werde ich treffen?“ „Einen, Frau Müller“. „Warum, Johnny?“ „Frau Müller, nach dem ersten Schuss fliegt der zweite Vogel weg.“ „Johnny, das ist die falsche Antwort, aber mir gefällt, wie du denkst.“
Am nächsten Tag kommt Johnny ins Klassenzimmer. „Frau Müller, mein Vater sagt, daß ich mein Taschengeld sparen soll. Ich habe eine Wahl: Eine Bank bietet mir eine pädagogische Broschüre. Die andere Bank hat eine sehr hübsche Kassiererin. Welche Bank soll mein Konto bekommen?“ Die Lehrerin lacht, und sagt: „Nun, vielleicht diejenige mit der sehr hübschen Kassiererin. Johnny erwidert: „Nein Frau Müller, die mit der größten Staatsgarantie, aber mir gefällt wie Sie denken!“
Freiheit und Handel sind eng verwandt. Ohne Freiheit gibt es keinen fairen Handel. Die Sicherheit, dass uns der Handel liefert, was wir zum Leben brauchen, gibt uns das Vertrauen in die Zukunft, ohne dass wir von der Angst um das Überleben gelähmt sind. Die Freiheit, im Handel zu konkurrieren hält uns innovativ und relevant. Wie Friedrich Hayek schon fest stellte, die Freiheit ist nicht das Gegenteil von Zwang, sondern Freiheit ist Ordnung durch das Gesetz. Wir sind heute hier, um unsere gemeinsamen Hanse Traditionen zu feiern – Verbindung von Freiheit und Handel.
Das Wesen der Freiheit und des Handels verändert sich rasant. Wer hätte vor zwei Jahrzehnten gedacht, dass wir die Inhalte unserer Dachböden und Keller bei eBay handeln? Wer hätte die Explosion der billigen Flüge voraussehen können? Und es werden noch viel mehr Veränderungen kommen – der anhaltende Aufstieg Asiens von Japan über Korea, nach China und jetzt in Indien, die Öffnung des Iran, die Europäische Flüchtlingskrise, der Klimawandel, und wir blicken im Jahr 2050 auf Handel zwischen 10 Milliarden Menschen und Billionen von automatisierten Maschinen.
Während all dieser Veränderungen müssen unsere beiden Städte gemeinsam die Bedeutung der Freiheit und des Handels fördern. Wir haben eine moralische Verpflichtung, freie und wettbewerbsorientierte Märkte zu verteidigen. Die Gesellschaft hat viele Möglichkeiten zur Lösung von Krisen. Viele dieser Lösungen sind weder hübsch noch progressiv, sondern der Weg zur Leibeigenschaft. Der positive und direkte Weg, um Menschen in die globale Gemeinschaft zu bringen ist es, sie in die Welthandelsgemeinschaft einzubinden. Guter Handel macht gute Kameraden. Unsere Feier heute Abend ist ein freudiger Anlass, der als Erinnerung daran dienen soll, dass die Freiheit des Handels unsere Städte lebenswert macht.
Ich möchte mit einem Zitat aus der Antrittsrede von US-Präsident Thomas Jefferson schliessen – „Handel und ehrliche Freundschaft für alle”. Das Zitat ist das Motto meiner Gilde, der Worshipful Company of World Traders. Dieses Zitat verbindet unsere beiden Städte London und Hamburg. Darf ich Sie bitten, auf zu stehen, und einen Toast mit mir auf die Gesundheit der Freien und Hansestadt Hamburg zu trinken, „Handel und ehrliche Freundschaft für alle.”
“Freiheit des Geistes, der Chancen und des Handels”.
Morgensprache – English
15 October 2015, Handelskammer Hamburg
We from London wish to congratulate Hamburg on the continuing success of your Morgensprache celebrations. As a Professor of Commerce, I love a city that celebrates trade. Our two cities are fiercely independent. The Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg has been a proud city-state since the 9th century. The City of London is the oldest continuous democracy in the world. Our two cities are united in trade over the centuries. On 8 November 1266 a contract between Hamburg’s traders and Henry III of England establish a hanse in London – the first time in history the term was used for the League.
Our German connections are strong. My wife comes from Franken. My grandmother was German. But I’ve never given a formal speech, so I almost began, as they do in Franken, with ‘Gruss Gott’. We visit friends often in your ancient and vibrant city. I raced sailboats at Kieler Woche every year during the 2000s. My wife and I are in shipping with a commercial sailing boat and belong to the Worshipful Company of Watermen & Lightermen. But we never expected the honour of being asked to address you today. Thank you.
Our two cities are united in so much commerce – shipping, technology, finance, arts, media and publishing – but the most important thing that unites our cities is similar ways of thinking.
One day a teacher asks her student Johnny, ‘Johnny, if there are two birds on a wire and I fire two barrels from a shotgun, how many birds will I hit?’. ‘One, Miss’. ‘Johnny, please listen, if there are two birds on a wire and I fire two barrels from a shotgun, how many birds will I hit?’. ‘One, Miss’. ‘Why Johnny?’. ‘Well Miss, after you fire the first barrel the second bird will fly away.’ ‘Johnny, that’s the wrong answer, but I like the way you think.’
The next day Johnny comes into the classroom. ‘Miss, my Dad says that I must save my allowance. One bank offers me an educational booklet. The other bank has a very pretty teller. Which bank should get my account?’ The teacher blushes, and says ‘Well, perhaps the one with the very pretty teller.’ Johnny replies, ‘No Miss, the one with the biggest government guarantee, but I like the way you think!’.
Freedom and trade are strongly related. Without freedom there is no fair trade. The certainty and confidence that trade can deliver what we need to live gives us the confidence to think to the future, not paralysed by fear of surviving the present. The freedom to compete in trade keeps us innovative and relevant. Yet Friedrich Hayek notes that freedom is not the opposite of constraint, rather, “freedom is order through law”. We are here today to celebrate our mutual Hanseatic connections – bindings of freedom and trade.
The nature of freedom and trade is changing rapidly. Who would have thought two decades ago that we would be trading the contents of our attics and basements on eBay? Who could have foreseen the explosion of cheap air flights? And there is much more change to come – the continuing rise of Asia moving from Japan to Korea to China and now to India, the opening of Iran, the European refugee crisis, climate change, looking to commerce and trade in 2050 among 10 billion people trading with trillions of automated machines.
Throughout all of these changes, our two cities must mutually promote the importance of freedom and trade. We have a moral obligation to defend free and competitive markets. Society has many ways of resolving crises. Many of society’s ways of dealing with problems are neither pretty nor progressive, the roads to serfdom. The most positive and direct way to bring people into the global community is to bind people into the global trading community. Good trade makes good fellows. Our celebration tonight is clearly fun, but hopefully it provides a small reminder that freedom to trade makes our cities worth living in.
I would end with a quote from US President Thomas Jefferson’s inaugural speech of 1801 – “with commerce and honest friendship for all”. The quote is the motto of my Worshipful Company of World Traders. This quote unites our two cities of London and Hamburg. May I ask all of you to be upstanding and drink a toast with me to the health of the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, “with commerce and honest friendship for all.”
An ideas revolution
With unproven innovation utility and litigation costs exceeding licence income, as well as frivolous lawsuits, legal bullying, and patent portfolios barring market entry, patent reform is essential (“A Question Of Utility”, August 8th). Patent offices are 19th century fixed fee stamping machines. There is no redress against a patent office if a patent is poorly awarded. Patent offices ration resource inputs (bureaucratic time) rather than balance supply and demand with risk. Poor quality patent issuance is an economic externality borne by society through the legal system and innovation of the past.
It could be reformed through better economics: firstly, patent offices should auction a strict number of tradable options to file patents each year at a fixed application price. Option holders could decide to file and incur the application costs, or sell the application to others if they don’t care to use it. Secondly, patent offices should provide a legal indemnity offer alongside an awarded patent. If the patent is later successfully overturned in a designated court, then the patent office pays a fixed amount towards legal costs. Customers would evaluate patent offices on the cost of an option to apply, the application fee, the scale of indemnity offered, and the supplementary fee charged if they choose to take the insurance offer. Patents would be worth significantly more with such an indemnity, especially to smaller players. Thirdly, competition, why not have more than one patent office per nation offering competing indemnity levels? Combined, these three reforms would provide the economic information society needs to assess the quality and value of patent offices.
MICHAEL MAINELLI
Executive Chairman
Z/Yen Group Limited
London
27 August 2015 – https://www.economist.com/letters/2015/08/27/letters-to-the-editor
Kuring? No, But Konfirming The Origins Of Kawasaki Disease
Here is a nice story about the ancient Barts Pathology lab helping advance modern medical science a teensy bit over the tragic Kawasaki disease:
“Gee’s post-mortem examination findings, preserved in a single paragraph written in 1871, recorded signs of damage called aneurysms in the coronary arteries running across the surface of the boy’s heart.”
For me, this museum story began in 2006. Professor Will Ayliffe and I were aghast at the state of deliberate neglect when we made an ‘illegal’ tour of the then abandoned facility. I was on a board of the United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS) where the Clinical Pathology Association (CPA) was a subsidiary. The CPA had a Trust to which we applied for cataloguing, and the CPA Trust funding came through in 2009/2010 with Dr Ken Scott’s support (the CEO of CPA). Colleague Professor Adrian Newland lent his support, thus drawing in Barts Trust support.
The publication by Carla Connolly of her preservation work – http://www.ibms.org/includes/act_download.php?download=pdf/2012-March-St-Barts.pdf – along with this Gresham College lecture by Will – http://www.gresham.ac.uk/lectures-and-events/anatomy-museums-past-present-and-future – (supported by Gresham Professors Tim Connell and Frank Cox), and City of London support through Wendy Mead kept up the visibility, leading to the permanent museum arrangements with Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) – http://www.smd.qmul.ac.uk/about/pathologymuseum/
And it turned out the historic collection was useful, perhaps invaluable, as long suspected by Will and me. Sadly (for those with this rare disease and their families), yet hopefully (medically and scientifically), perhaps more value will be derived in future on Kawasaki and other diseases. I think it is a great story, or backstory, for all of us in the City, Gresham College, and the scientific profession.
[Coda: during the covid-19 pandemic we have also seen Kawasaki disease feature, so the origins are important –
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)31129-6/fulltext
https://www.nbcnewyork.com/news/local/a-pretty-scary-thing-rare-child-syndrome-tied-to-virus-worries-new-york-100-sick/2413952/]
Sirius-ly Long But Successful-ly
One of my longer and more problematic projects has been Sirius Minerals. What began as a copper and gold mining exploration firm turned into one of the biggest potash firms, and the first non-hydrocarbon mine in the UK in over half a century. As I’ve remarked to friends, if oil & gas run out we wind up cycling, but if the potash runs out we move from 7 billion people to 1 billion people in less than two years. Hmmm.
Planning permission has been the key to success. Having been one of the founders, along with Richard Poulden and Jonathan Harrison, back in 2005, I was delighted to see planning permission finally approved.
FT Coverage – http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/a70a4568-1f4f-11e5-ab0f-6bb9974f25d0.html
Guardian Coverage – http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2015/jun/30/north-york-moors-potash-mine-gets-17bn-go-ahead
It’s an exciting, interesting (not least being a two century export supply for all of Europe and having a 37 km transportation tunnel to Teeside), and potentially highly-profitable project with which I’m proud to have been associated. Interesting that it becomes successful alongside another decade long project at Barts (see next). The pigeons may take a long time to come home to roost, but they do home in.
Aldermanic Assessment
In these days of continuous assessment, how do you know where you stand? For folks in the City you could do worse than look into the Liber Albus 2015 (White Book 2015). So what am I to make of this contribution to the book?
A bit frightening that I appear to be increasing the City of London Corporation’s repair bills. Perhaps I’ll fare better in next year’s annual review.
To order a copy – CITY WHITE BOOK 2015 – ORDER FORM
Tired in London or Tired of London?
Samuel Johnson’s famous remark went – “Why, Sir, you find no man, at all intellectual, who is willing to leave London. No, Sir, when a man is tired of London, he is tired of life; for there is in London all that life can afford.”
Johnson made this remark to his biographer, Boswell (who interestingly lived in Scotland throughout their relationship), on 20 September 1777. Not a lot has changed. My dear friend and former mathematics teacher, Bill Joseph, retired to London citing three big reasons, Gresham College (intellectual), the National Health Service, and free Transport for London passes. Same idea as Johnson’s I’d guess.
So 239 years later, how does London look for the world weary? Johnson may have been correct about “tired of London”, but that doesn’t mean you can’t easily become “tired in London”. What an exhausting and interesting month for us. So exhausting that this piece is more a photo album of things we did than any form of essay. First, we got out of London in early May, up to Boswell country in Scotland, and spent the election day (yes, did a postal ballot), revisiting things since the last Scottish trip (which coincided with another election, the Referendum).
Eric Smith, pictured above, delivered a great engineering experience around the idea of sailing, though with 45 knot winds, five degree weather, and a diesel engine that knew more about breathing air than combusting air, most of the time was spent either sailing a nine-tonne boat onto a berth without power or down in the fumes of the engine room than sailing ‘towards’ Campbelltown for some whisky tasting. Perhaps next year, on a Caledonian MacBrayne ferry.
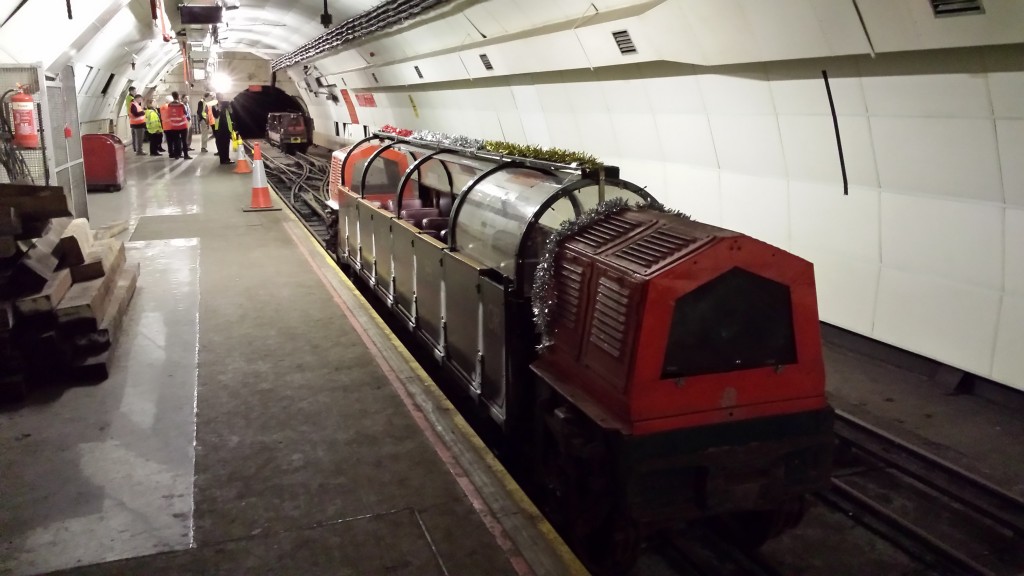

Then more engineering as my daughter and I went to see the state of the “Mail Rail”. I first saw the Mail Rail working in 1986 underneath the old General Post Office headquarters, now the King Edward Building, on St Martin’s le Grand. I’ve been a (minor) patron of getting this rail working again and am delighted that the British Postal Museum & Archive have succeeded in raising the funds to do so.
It will be a major tourist attraction in a couple of years, whisking people on a 15 round-trip journey. Though as my daughter explained it’s really for tourists – “Daddy, as Londoners we see a lot underground platforms”.
On 14 May there was a magnificent celebration of the 800th anniversary of the London Mayoral Charter (9 May 1215) and of the 800th year of the Magna Carta, a nice counterpoint to some Magna Carta Gresham talks I arranged earlier in the year. The commemoration was a service held in Temple Church, then Middle Temple for drinks, then Inner Temple for dinner. Moving choral services, touching sermons, and fantastic hospitality (and wines). In the lectures earlier this year, Lord Igor Judge emphasised the pivotal role of William Marshal, Earl of Pembroke, in the Magna Carta, so it was very touching to have this event with him entombed in Temple Church beside us. I hadn’t fully appreciated the central role of Temple Church and the Templars in the Magna Carta negotiations.
The Temple Church was built by the Knights Templar, an order of military monks founded in 1118 to protect pilgrims to the Holy Land. Here in the Temple the Templars had their Church, two halls, cloisters and domestic buildings, leading in the 12th century straight down to the River Thames. The Round Church was built soon after 1160; it is the earliest Gothic building in England. In the crisis of 1214-5 King John had two London headquarters: the Tower in the East; and the Temple in the West, where he was safe under the protection of the Templars. The Round Church was in use by 1162. It is the earliest Gothic building in England. It was modelled on the circular Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, the site of Christ’s death, burial and rising; to be in the Round Church was, to the medieval imagination, to be in Jerusalem, at the holiest place in the world. Here’s the timeline in full (courtesy of Geoff Pick, Archivist, City of London Corporation):
- 10 February 1185 – The Round Church was consecrated by Heraclius, Patriarch of Jerusalem, in London to ask King Henry to take on the kingship of Jerusalem.
- 1204 – King John lost Normandy, Anjou and Poitou to King Philip of France. John’s campaigns to recover them led to ever higher taxes.
- March 1213 – The King finalised a treaty with his Continental allies at the Temple, and then deposited 20,000 marks here for his ambassadors.
- May-July 1213 – The King submitted to the Pope. Archbishop Stephen Langton returned to England. For the negotiations, the King was staying at the Templars’ house near Dover. William Marshal, Earl of Pembroke was witness and guarantor to the King’s submission. The King’s excommunication was lifted, and in return he offered a golden mark which he borrowed from the Master of the Temple.
- 3 October 1213 – The King was at the Temple, to confirm at St Paul’s Cathedral that the Pope was now the feudal lord of the King and his kingdom.
- 27 July 1214 – The Battle of Bouvines. With this defeat John lost all prospect of the recovery of his French possessions.
- 16-23 November 1214 – The King was in the Temple. On 21 November he issued from the Temple the charter granting ‘with the common consent of our barons’ free elections to cathedral and conventual churches, and on 22 November a grant to St Paul’s Cathedral.
- 7-15 January 1215 – The King was in the Temple. A group of barons, armed and ready for war, confronted him. According to the barons’ account of this seminal week, they asked the King to confirm their ancient and accustomed liberties but he refused, and in turn he asked them to give a written undertaking on behalf of themselves and their successors that they would never in future demand such liberties. The barons, lacking a prince to claim or put upon the throne, were demanding the King’s own allegiance to a charter. John sought refuge in delay; such innovation, he said, would take time. The barons gave him warning: they were pledging themselves, one and all, as a wall of defence for the house of the Lord and would stand firm for the liberty of the Church and the realm. The barons rightly distrusted the King: during the negotiations themselves John sent emissaries (surely secretly) to the Pope. John gave the barons a safe conduct until after Easter; William Marshal and the Archbishop were among the King’s guarantors, assuring the barons that the King would then give them satisfaction.
- 15 January – The cathedral and convent charter of 21 November 2014 was reissued from the Temple.
- 16-22 April 1215 (Eastertide) – The King was in the Temple.
- 7-9 May 1215 – The King was in the Temple. On 9 May the charter was issued from the Temple that guaranteed to the City of London the right freely to elect its own Lord Mayor. “Know that we have granted, and by this our present writing confirmed, to our barons of our city of London, that they may choose to themselves every year a mayor, who to us may be faithful, discreet, and fit for government of the city, so as, when he shall be chosen, to be presented unto us, or our justice if we shall not be present.” The Lord Mayor still processes on the day of his or her installation to the Royal Courts of Justice to appear before the Lord Chief Justice.
- 17 May 1215 – The barons captured London. The balance of power now lay against the King; he must negotiate.
- 28 May 2015 – The King received the imperial regalia of his grandmother the Empress Matilda from the custody of the Master of the Temple. He was going to assert his full majesty at the coming conference.
- 10 June 1215 – The King arrived at Runnymede.
- 15 June 1215 – The King sealed the Charter. William Marshal Earl of Pembroke and Brother Aymeric, Master of the Temple, were listed among those who had advised the King. The Earl’s eldest son and Serlo the Mercer, Mayor of London, were two of the Twenty-Five surety barons, appointed to ensure the King’s conformity to the Charter’s terms.
- 19 October 1216 – King John died. The King’s Council named William Marshal the guardian (rector) of the young King Henry III and of the realm.
- 12 November 1216 – The Earl of Pembroke reissued the Charter under his own seal.
- 6 November 1217 – The Earl of Pembroke again reissued the Charter under his own seal. Particular clauses were removed and issued separately as the Charter of the Forest; the remaining reissued clauses from 1215 were from now on known as the Great Charter.
- 14 May 1219 – The Earl of Pembroke died, and was buried on 20 May in the Temple’s Round Church. The Archbishop of Canterbury presided. Brother Aymeric, who had visited the Earl on his deathbed at Caversham, had wished to be buried next to the Earl; ‘I have enjoyed his fellowship on earth and hope to enjoy it also in heaven.’ On his return to London Aymeric fell ill and pre-deceased the Earl. He and the Earl were buried next to each other in front of the rood-screen between Round and chancel.
- 1224 – William Marshal the Younger, 2nd Earl of Pembroke married Eleanor, sister of King Henry III.
- 1225 – King Henry III reissued the Great Charter, in order to secure a grant of taxation.
- 1235-1236 – Henry III and Queen Eleanor bequeathed their bodies to the Templars. The Templars replaced the small chancel of the Temple Church with the present hall church to be the burial place of the King and Queen. The new chancel was dedicated on Ascension Day 1240 in the presence of the King. Light, airy and simple, it is among the most beautiful of all Early English Gothic churches. (Henry III was in fact buried in Westminster Abbey, the Queen in Amesbury.)
- 1237, 1244, 1251 – A grant of taxation was made to the King upon the confirmation of the Charter. The meeting of the Great Council in 1237 was described as a Parliament, the word’s first use in the vocabulary of our constitution.
- Summer 1258 – The Council established by the Provisions of Oxford met daily, in the Temple and elsewhere, ‘spending wakeful nights,’ the Pope was told, ‘to prepare peace for others.’
- March 1259 – The Council proclaimed in the Temple its first set of proposals, the foundational Provisions of the English Barons, ‘on account of the common good of the whole realm and of the King himself’. The King summoned Parliament to the Tower, demanding that the barons come unarmed. The barons refused, and insisted on Westminster. Parliament in fact met at the Temple, a compromise safe for both sides.
- 12 October 1297 – Edward I re-issued the Great Charter. An official copy was for the first time enrolled by the Chancery and copied into the earliest of the Chancery’s Statute Rolls as an official enactment of the text.
It felt only appropriate to round this tiring month off to check on what those Royals are now up to, with a visit to Buckingham Palace for tea:
Whew!